At SYNTHESIS Orthopaedics & Joint Replacement Clinic in Navi Mumbai, Dr Suyog Chavhan and our team of experts understand how arthritis can impact your daily life. Our goal is to provide comprehensive, personalized care that helps you manage and alleviate symptoms, enabling you to live a more comfortanavible, active life.
What is Polyarthritis?
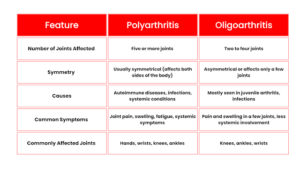
Polyarthritis refers to inflammation in five or more joints simultaneously. It is a condition that often indicates a more widespread or systemic issue affecting multiple joints, and it can be a sign of an autoimmune disorder. The inflammation can affect any joint in the body, including the hands, wrists, knees, and ankles.
Common Symptoms of Polyarthritis:
- Multiple joint pain and swelling: Pain, stiffness, and swelling affecting several joints at once.
- Symmetrical involvement: Often affects joints on both sides of the body equally.
- Morning stiffness: Joints are especially stiff after waking up, and it can take time to loosen up.
- Fatigue: Due to the systemic nature of the condition, fatigue can often accompany joint inflammation.
- Fever and weight loss: In some cases, polyarthritis may be associated with systemic symptoms like fever and unintentional weight loss.
Causes of Polyarthritis:
- Rheumatoid arthritis (RA): An autoimmune disease where the body attacks its own joints.
- Psoriatic arthritis: A type of arthritis linked with psoriasis.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Another autoimmune condition that can cause polyarthritis.
- Infectious arthritis: Sometimes, an infection in the body can lead to polyarthritis.
What is Oligoarthritis?
Oligoarthritis, on the other hand, involves inflammation in two to four joints. It is often seen in children and can be a hallmark of juvenile arthritis, although adults can also develop it in specific conditions.
Common Symptoms of Oligoarthritis:
- Pain and swelling in a few joints: Generally, only two to four joints are affected.
- Asymmetrical involvement: Unlike polyarthritis, oligoarthritis may affect only one side of the body or a limited number of joints.
- Joints most affected: Knees, ankles, and wrists are commonly affected.
- Less systemic involvement: There may be less fatigue and systemic symptoms compared to polyarthritis.
Causes of Oligoarthritis:
- Juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA): The most common cause of oligoarthritis in children.
- Reactive arthritis: Caused by infections elsewhere in the body.
- Infection-related arthritis: Some bacterial infections may lead to oligoarthritis.
Key Differences Between Polyarthritis and Oligoarthritis
Treatment Options for Polyarthritis
Treating polyarthritis often requires a multifaceted approach that addresses both pain relief and managing the underlying condition. Since polyarthritis is often linked to autoimmune diseases, treatments may include:
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs): Medications like methotrexate and hydroxychloroquine can help slow the progression of autoimmune-related arthritis.
- Biologic drugs: Targeted therapies that block specific parts of the immune system involved in joint inflammation.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): To reduce pain and inflammation.
- Corticosteroids: For short-term flare-ups to reduce inflammation quickly.
Treatment Options for Oligoarthritis
Since oligoarthritis typically affects fewer joints, the treatment approach is often less aggressive. The goal is to control the inflammation and prevent long-term joint damage:
- NSAIDs: To reduce inflammation and manage pain.
- Physical therapy: Helps improve joint mobility and strengthen muscles around the affected joints.
- Corticosteroids: Can be injected directly into the affected joints to control inflammation.
- Disease-modifying treatments: In cases like juvenile idiopathic arthritis, DMARDs or biologics may be used if the condition is persistent.
When to Seek Medical Help
If you experience symptoms like joint pain, swelling, or stiffness that don’t improve or worsen over time, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent joint damage and improve long-term outcomes. At SYNTHESIS Orthopaedics & Joint Replacement Clinic, Dr. Suyog Chavhan specializes in diagnosing and treating both polyarthritis and oligoarthritis. We provide personalized treatment plans designed to alleviate pain and improve joint function.
Conclusion
Polyarthritis and oligoarthritis may seem similar at first glance, but understanding their key differences can lead to better management and treatment. Whether you’re dealing with the widespread effects of polyarthritis or the more localized pain of oligoarthritis, SYNTHESIS Orthopaedics & Joint Replacement Clinic is here to guide you. Dr. Suyog Chavhan and our dedicated team will work with you to develop a tailored treatment plan that meets your needs and improves your quality of life.
If you’re experiencing joint pain or inflammation, don’t wait. Reach out to us today and take the first step toward better joint health.
📍 Visit us at: SYNTHESIS Orthopaedics & Joint Replacement Clinic
📞 Call Now: +91 9082633731
📧 Email: drsuyogchavhan@gmail.com




